
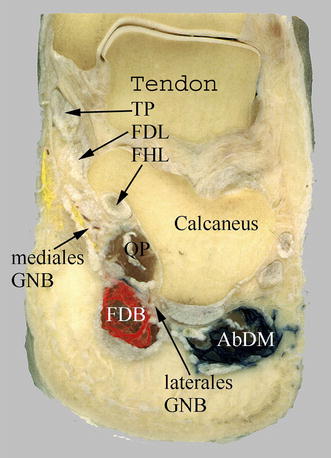
It is common that muscles of a certain area will share innervation and vascularization. Namely, the deep flexor muscles of the leg are: Additionally, the natural tension of these muscles, especially the tibialis anterior, supports the medial arch of the foot. Generally, their main functions are plantarflexion, inversion of the foot, and flexion of the toes. The posterior muscles are natural antagonists to the anterior muscle group. The deep muscles are separated from the superficial layer by a deep layer of fascia. Plantar extension of foot, Plantarextensio pedis Gastrocnemius, Plantaris, Soleus (deep group) Tibialis posterior, Flexor hallucis longus, Popliteus, Flexor digitorum longus) Great Plans Sometimes Tie Friends and Partners Forever Insertion: Tuberosity of navicular bone, All cuneiform bones, bases of metatarsal bones 2-4 (Cuboid bone)įunction: Talocrural joint: Foot plantar flexion Subtalar joint: Foot inversion Supports medial longitudinal arch of foot Origin: Posterior surface of tibia, Posterior surface of fibula, Interosseous membrane Insertion: Bases of distal phalanges of digits 2-5įunction: Metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints 2-5: Toe flexion Talocrural joint: Foot plantar flexion Subtalar joint: Foot inversion Origin: Posterior surface of tibia, (inferior to soleal line) Insertion: Base of distal phalanx of great toeįunction: Metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joint 1: Toe flexion Talocrural joint: Foot plantar flexion Subtalar joint: Foot inversion Origin: (Distal 2/3 of) Posterior surface of fibula, Interosseous membrane Insertion: Posterior surface of proximal tibiaįunction: Unlocks knee joint Knee joint stabilization Origin: Lateral femoral condyle, Posterior horn of lateral meniscus of knee joint Key facts about the deep posterior muscles of the leg This article will discuss the anatomical properties that the deep posterior muscles of the leg share, and as well as the clinical states related to them. For this reason, the posterior compartment is subdivided further into superficial and deep muscle groups.

The posterior group is strongly developed due to the consistent resistance to gravity while standing, walking, jumping, and so on.įor all of those actions, the muscles of the posterior compartment need to be strong and numerous. Grossly speaking, there are three major compartments of the leg: anterior, lateral, and posterior.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
